
Cho-il Kim
Korea Health Industry Development Institute, South Korea
Title: Dietary exposure of the Korean population to acrylamide and furan: Total diet study
Biography
Biography: Cho-il Kim
Abstract
Introduction & Aim: Acrylamide (AA) and furan (F) have been classified as probably carcinogenic (group 2A) and possibly carcinogenic (group 2B) respectively by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. They are produced by Maillard reaction during production, processing, and/or cooking of foods, unintentionally. With the recent amendment on the Food Sanitation Act in Korea, the Ministry of Food & Drug Safety decided to evaluate dietary exposure of the Korean population to those hazardous materials produced involuntarily throughout steps from farm to fork. Hence, we attempted to estimate AA and F exposure of the Korean population and assess the relevant risk.
Materials & Methods: Using the dietary intake data of individuals collected through nutrition survey component of the Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, we established a nationwide representative data set of six years from 2008 through 2013. To draw a representative food list for total diet study, we considered foods consumed in higher amount, foods consumed by more people more frequently, and foods contributes more to fat intake (figure 1) resulting in a list covering 97.4% of mean food intake. Based on the type of dishes (cooked foods), about 1,200 pairs of ‘food X cooking methods’ were identified for chemical analysis sample preparation. AA was analyzed using LC/MS and automated HS-SPME-GC/MS was used for F analysis.
Results: Mean exposure to AA and F were estimated to be 0.086 μg/kg bw/day and 0.210 μg/kg bw/day, respectively. Corresponding MOE values (2,045-3,522 and 4,137 based on the BMDL10 set by JECFA) fell into the category of possible concern. Food contributes the most to AA exposure was black pepper (18.2%), and only five foods were needed to cover half of AA exposure in contrast to more than a dozen of foods in F exposure.
Conclusion: Korean government is working on measures to minimize the exposure.
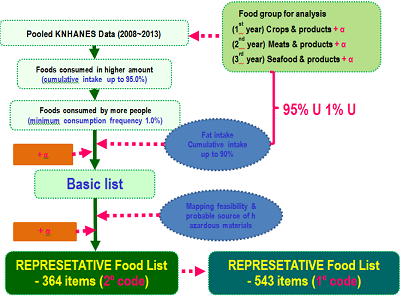
Figure 1. Flow of representative food selection process

